Inflammation is a natural and necessary response of the body to injury or infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on our health, contributing to a range of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The good news is that our diet plays a significant role in managing inflammation and restoring the body's balance. By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into our meals, we have the power to combat chronic inflammation and promote overall well-being. These foods possess unique properties that can soothe and support the body's healing processes, offering a natural and effective way to enhance our health.

Anti-Inflammatory Index
Jump to:
- What is inflammation?
- Introduction to anti-inflammatory foods
- What causes inflammation?
- Health risks of chronic inflammation
- Lifestyle intervention for reducing inflammation
- Dietary intervention for reducing inflammation
- Foods to avoid
- Foods to include
- Eating tips for reducing inflammation
- Sample 1-day anti-inflammatory meal plan
- Anti-inflammatory foods summary
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural protective response triggered by the immune system to combat injury, infection, or irritation. When the body detects harmful stimuli, such as pathogens or damaged cells, it releases immune cells, hormones, and chemical mediators to the affected area, leading to increased blood flow, swelling, warmth, and redness. This acute inflammation is a crucial defense mechanism that helps remove the source of harm and initiate the healing process.
However, when inflammation becomes chronic or persists for extended periods, it can contribute to various diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, autoimmune conditions, diabetes, arthritis, and even certain cancers.
Chronic inflammation can result from factors such as poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, smoking, and obesity. Managing inflammation and promoting a healthy balance is essential for maintaining overall well-being and preventing long-term health complications.

Introduction to anti-inflammatory foods
From vibrant fruits and vegetables bursting with antioxidants to omega-3-rich ingredients and wholesome whole grains, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into our diet plays a vital role in reducing inflammation and achieving optimal health.
Inflammation is an important part of the body's natural immune response and can be beneficial to protect tissues, increase blood flow and support wound healing. When inflammation persisted longer than necessary, it may hinder the healing process.
The anti-inflammatory diet is less about food restriction, but rather, it details the foods you can eat more of. The aim is to increase antioxidant levels and dietary fiber while minimizing or eliminating refined and processed foods and promoting a lower omega-6 to omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio.
The purpose of an anti-inflammatory program is to:
- Promote foods that can help reduce inflammation
- Minimise foods that may encourage an inflammatory environment
- Support optimal digestive function for effective and efficient nutrient digestion and absorption
What causes inflammation?
Inflammation can be caused by various factors, including:
- Poor diet high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats
- Chronic stress
- Lack of physical activity
- Lack of sleep and rest
- Environmental toxins
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Chronic diseases such as obesity

Health risks of chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation has been linked to several health risks, including:
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Elevated blood pressure
- Impaired insulin sensitivity and increased risk of diabetes
- Weight gain and obesity
- Increased risk of certain cancers
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Digestive disorders
- Weakened immune system

Lifestyle intervention for reducing inflammation
In addition to dietary modifications, incorporating the following lifestyle changes can further help manage inflammation:
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise can reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for at least 3 hours of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Manage stress: Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities you enjoy.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night to support your body's healing and recovery processes.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol can increase inflammation in the body.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body weight, especially around the waist, can contribute to chronic inflammation. Adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.

Dietary intervention for reducing inflammation
There are several dietary interventions that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Here are some key recommendations:
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your diet, especially those rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables. These foods help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Consume foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and can help balance the body's inflammatory response.
- Healthy fats: Opt for healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, and nuts. These contain monounsaturated fats, which have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Whole grains: Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. Whole grains contain fiber and other nutrients that have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Spices and herbs: Incorporate anti-inflammatory spices and herbs into your cooking, such as turmeric, ginger, garlic, cinnamon, and rosemary. These ingredients have been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Limit processed foods: Reduce your intake of processed and refined foods, including sugary snacks, fast food, and processed meats. These foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and artificial additives, which can promote inflammation.
- Avoid trigger foods: Identify and avoid any specific foods that may trigger inflammation or cause adverse reactions in your body. This can vary from person to person, so it's essential to pay attention to your individual responses
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress levels, getting regular exercise, and obtaining adequate sleep are also crucial for reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.

Foods to avoid
To reduce inflammation, it is advisable to avoid or limit the consumption of:
- Processed foods high in refined sugars, trans fats, and artificial additives
- Fried foods and fast foods
- Excessive consumption of red meat and processed meats
- Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pasta, pastries, etc.)
- Sugary foods and beverages
- Excessive alcohol
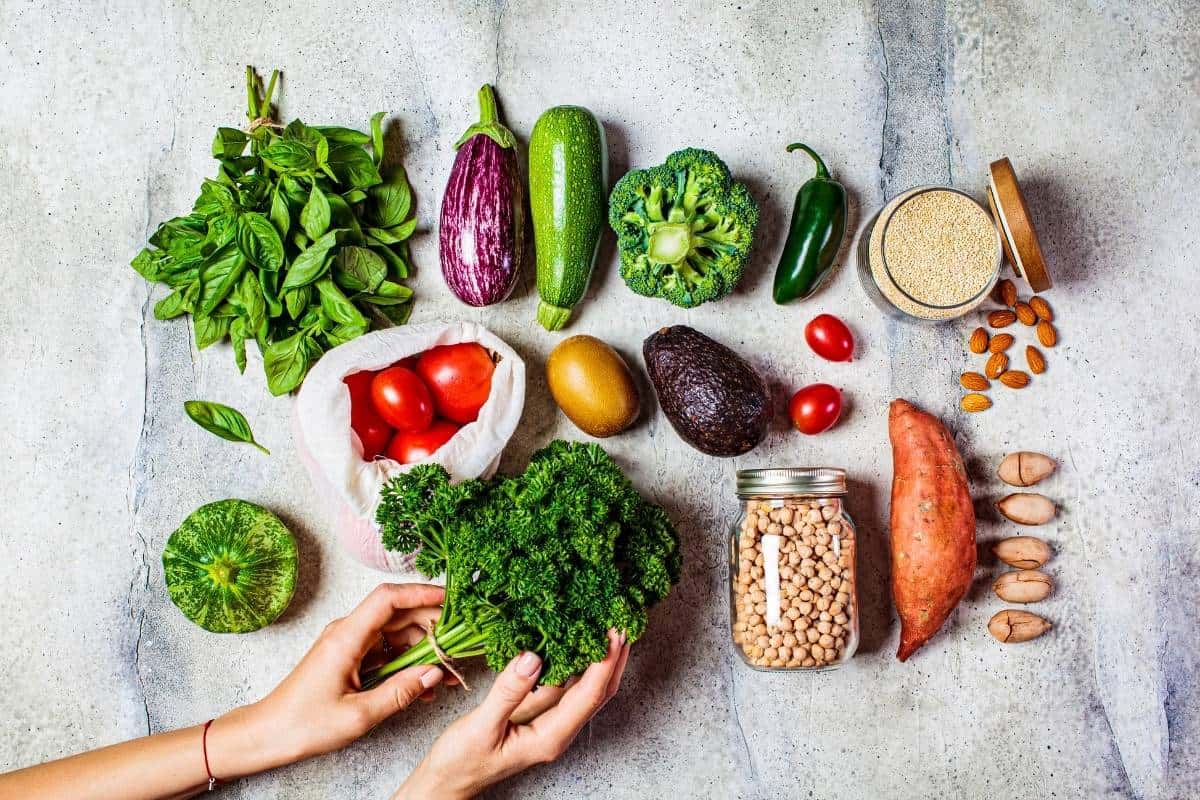

Foods to include
Including the following anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation and promote better health:
- Fruits: Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), cherries, oranges, and grapes
- Vegetables: Leafy greens (spinach, kale, broccoli), cruciferous vegetables (cauliflower, Brussels sprouts), peppers, and sweet potatoes
- Healthy fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts), and seeds (flaxseeds, chia seeds)
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout (rich in omega-3 fatty acids)
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and soybeans
- Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat
- Herbs and spices: Turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon
Learn about healthy plant-based fats here

Eating tips for reducing inflammation
- Eat slowly and mindfully: tune into your hunger levels
- Chew your food to allow for better digestion
- Do not eat food two hours before bedtime
- Persevere: never give up. Long-term lifestyle change is challenging. Try to enjoy the process, be kind to yourself, and cook as much of your own food as possible.
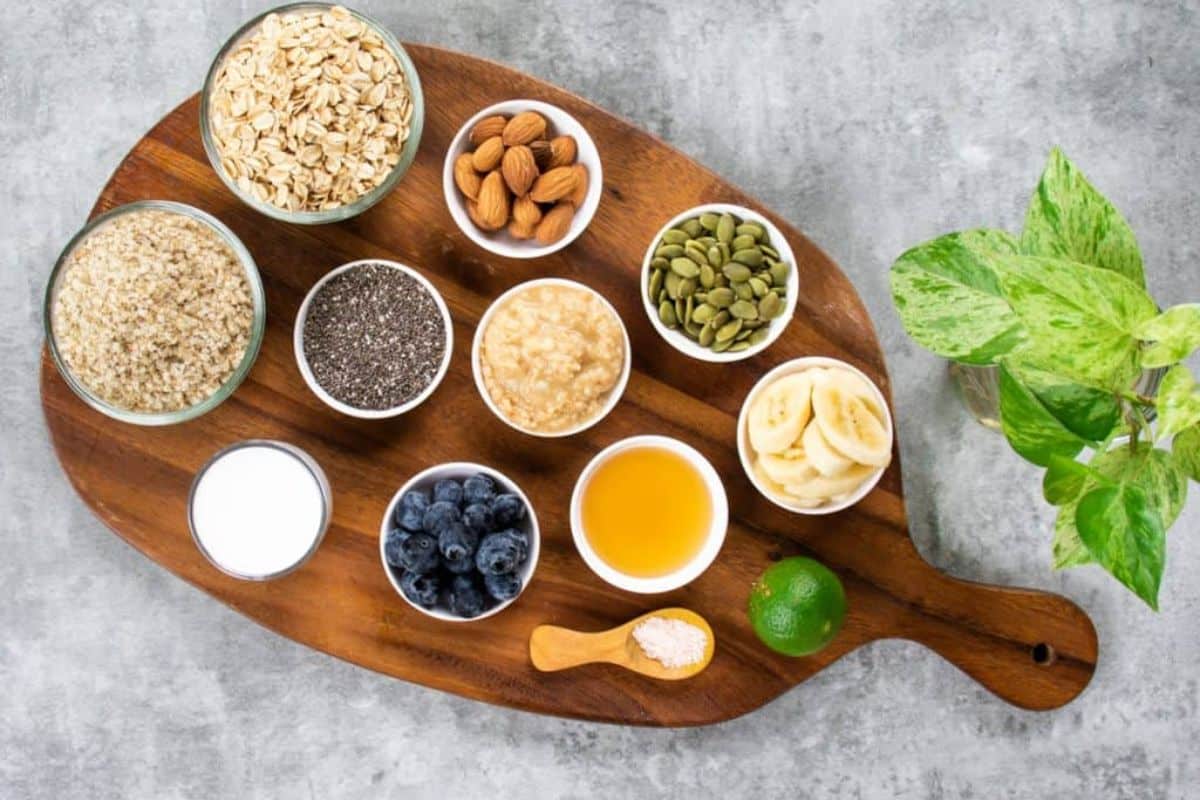

Sample 1-day anti-inflammatory meal plan
Here is a sample 1-day plant-based meal plan for reducing inflammation:
Breakfast:
- Overnight oats with rolled oats, almond milk, a tablespoon of ground flaxseeds, sliced bananas, and a sprinkle of cinnamon.
- Green tea or herbal tea.
Snack:
- Sliced cucumber and carrot sticks with a side of hummus.
Lunch:
- Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables (such as cherry tomatoes, cucumber, bell peppers, and spinach) dressed with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Steamed broccoli on the side.
- A cup of green tea or ginger tea.
Snack:
- A small handful of almonds or mixed nuts.
Dinner:
- Baked sweet potato topped with sautéed kale and chickpeas, seasoned with garlic, turmeric, and cumin.
- Mixed green salad with a variety of vegetables (such as lettuce, cherry tomatoes, grated carrots, and sliced radishes) dressed with a homemade vinaigrette (olive oil, apple cider vinegar, Dijon mustard, and a touch of maple syrup).
- Herbal tea or a glass of unsweetened almond milk.
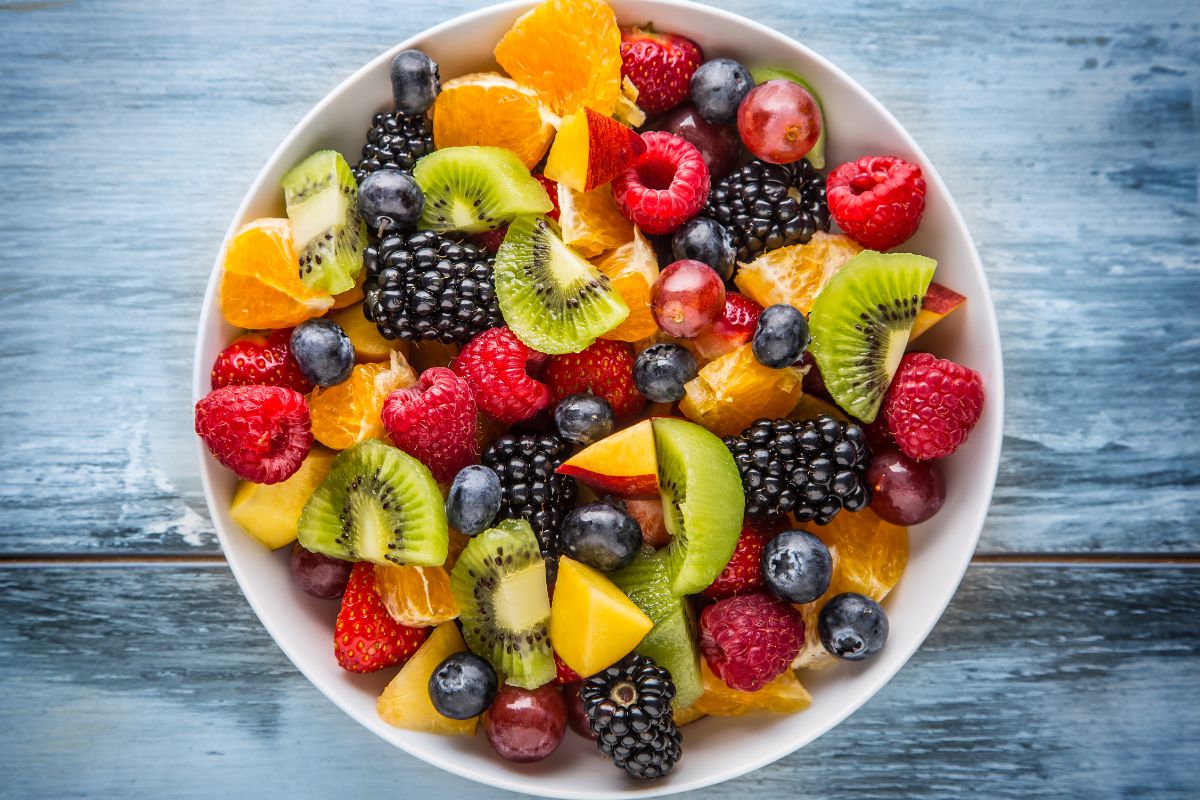
Dessert (optional):
- Fresh fruit salad with a sprinkle of cinnamon.
Hydration:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
Remember to adjust portion sizes and make any modifications according to your personal preferences and dietary needs. Enjoy a variety of nutrient-rich foods throughout the day.
If you would like to learn more about what Wellness Cuisine is, explore our article here.

Anti-inflammatory foods summary
By understanding the causes of inflammation, the health risks associated with chronic inflammation, and making appropriate menu and lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce inflammation, improve their overall health, and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into a well-rounded menu, along with practicing healthy lifestyle habits, can lead to significant benefits in managing inflammation.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to create a personalized anti-inflammatory plan that meets individual needs and goals.






Did you make this recipe? Let me know!